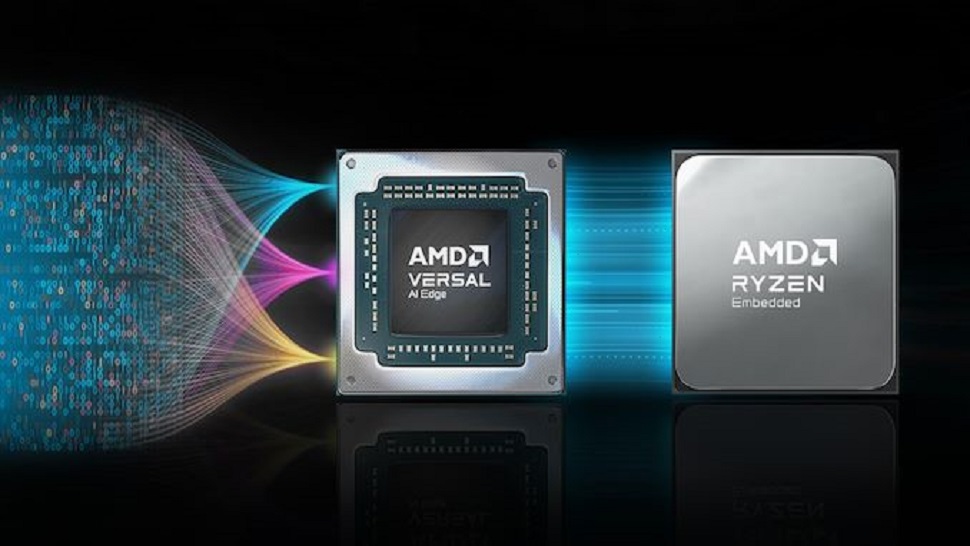
AMD’s Embedded platform, which is not talked about much like their desktop and server stuff, is important for devices like machines used in factories, cars, medical tools, gaming machines, and lightweight computers. AMD has just introduced Embedded+, a new setup that combines Ryzen Embedded processors with Versal adaptive SoCo on one board.
Table of Contents
The Embedded+ setup combines AMD’s Embedded processors with their Versal AI Edge adaptive SoCs on one board. AMD focuses on places where good computing power and energy efficiency are needed. This mix helps Embedded+ deal with tasks like AI processing and managing complex sensor data quickly, which is important for fast-moving and tough environments.
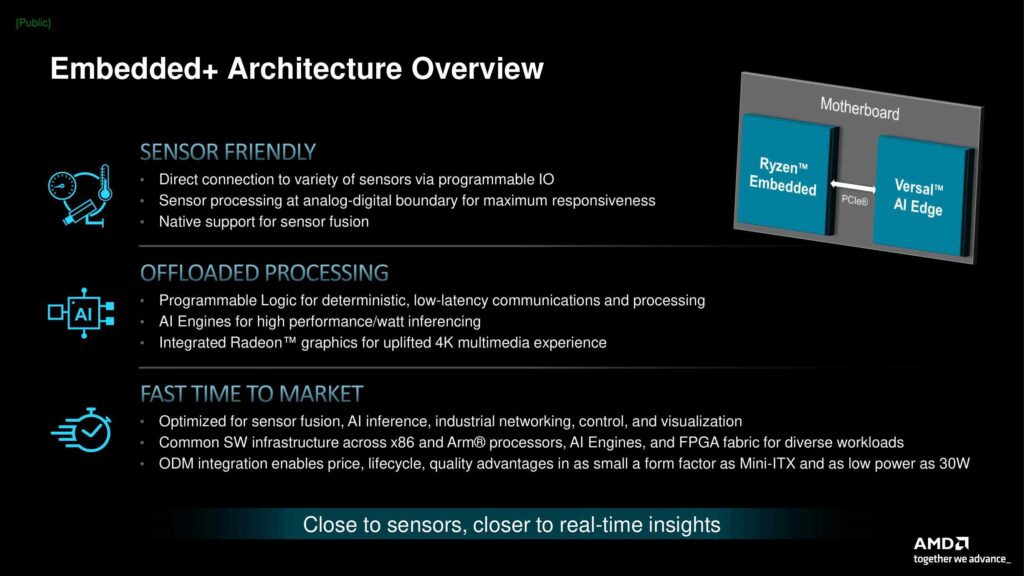
Giving companies that design products (ODMs) the chance to put both Ryzen Embedded and Versal SoCo on one board is really useful for industries that need quick responses between hardware and software. This includes self-driving cars, medical tools, and precise machines in factories. The AMD Embedded+ design can handle different kinds of tasks using various processors, like x86 and ARM, as well as AI operations and FPGA fabric. This helps a lot in making flexible and scalable computer solutions for different industries.
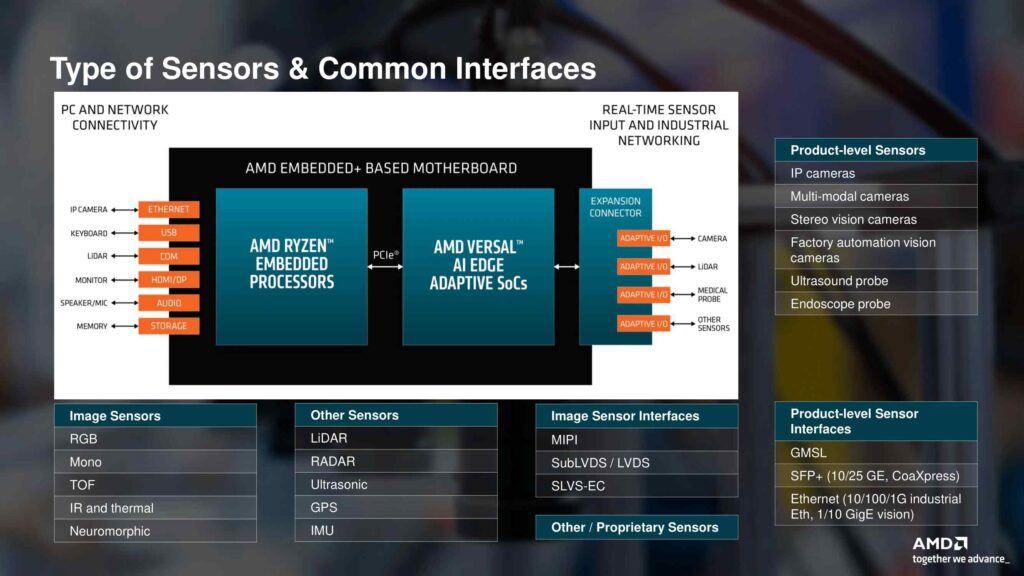
The AMD Embedded+ platform works well with many different kinds of sensors and how they connect. It’s easy to hook up regular devices and industrial sensors using Ethernet, USB, and HDMI/DP connections. The AMD Ryzen Embedded processors in the setup can deal with inputs from basic image sensors like color and black-and-white ones, and even more advanced types. They also handle standard ways that image sensors connect, like MIPI and LVDS.
Making it even better, the AMD Versal AI Edge adaptive SoCo on the Embedded+ motherboard give you flexible options for connecting sensors and industrial networks quickly. This means they can work with LiDAR, RADAR, and other important sensors in industries like manufacturing, healthcare and cars. The platform also supports different ways sensors connect, like GMSL and Ethernet-based vision protocols. This makes it a good fit for complex systems that rely on sensors.

AMD has also unveiled a new ready-to-use solution, available for product designers from today onwards. The Sapphire Technology VPR-4616-MB is a small motherboard in Mini-ITX from that combines the AMD Versal AI Edge 2302 SoC with an AMD Ryzen Embedded R2314 processor. The processor has 4 cores and 4 threads, along with 6 Radeon Vega compute units. This motherboard has a special connector for adding extra boards, offering various connection options, like two DDR4 SO-DIMM slots with up to 64 GB capacity, one PCle 3.0 x4 M.2 slot, and one SATA port for regular hard drives and SSDs. Additionally, the VPR-4616-MB comes with good networking features, including a 2.5 Gb Ethernet port and an M.2 Key E 2230 PCIe x1 slot for a wireless connection. It also supports the Linux-based Ubuntu 22.04 operating system.
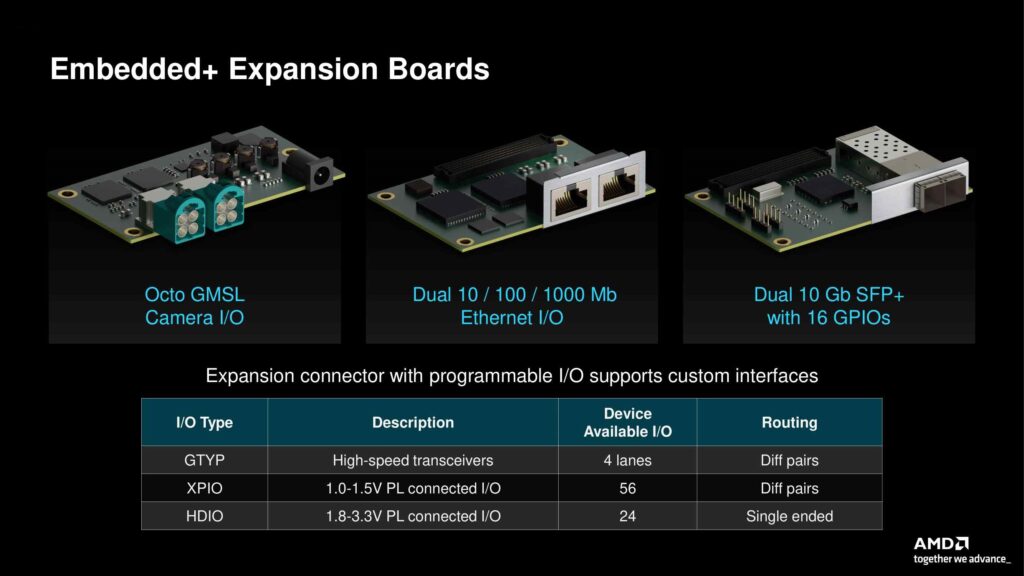
Also, revealed are a set of expansion boards that greatly expand support for the Embedded+ setup. The Octo GMSL Camera I/O board stand out for its capability to connect with multiple cameras at once. This is especially useful for systems relying on high-speed vision, crucial in fields like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and automated surveillance. Such systems often need to process and analyze many images in real-time, and the Octo GMSL board is designed specifically to meet this need.
Also, there’s a dual Ethernet I/O board ready for use. It supports 10/100/1000 Mb connections, ideal for places needing fast network communication. There’s also a Dual 10 Gb SFP+ board with 16 GPIOs for even faster data needs, suitable for tasks like real-time video streaming and handling lots of sensor data. These add-ons expand what the Embedded+ setup can do in industrial and edge settings.
The Sapphire VPR-4616 is now available for purchase. You can get it as a complete system with storage, memory, power supply, and casing.
Features: AMD Embedded + Architecture
- The AMD Embedded+ merges Ryzen for the CPU and Versal for the FPGA onto one signal circuit board.

- A Key thing about the new product is that it’s made for handling sensors. It uses the x86 and FPGA components for optimal performance.
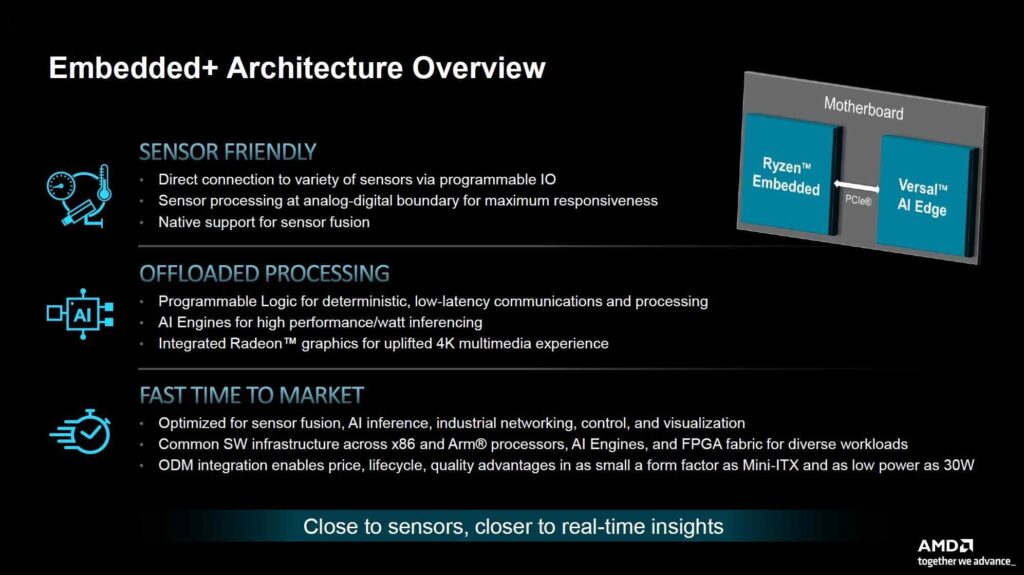
- You can see from the pictures above and below that there are two separate parts. They are joined together using something called PCIe.
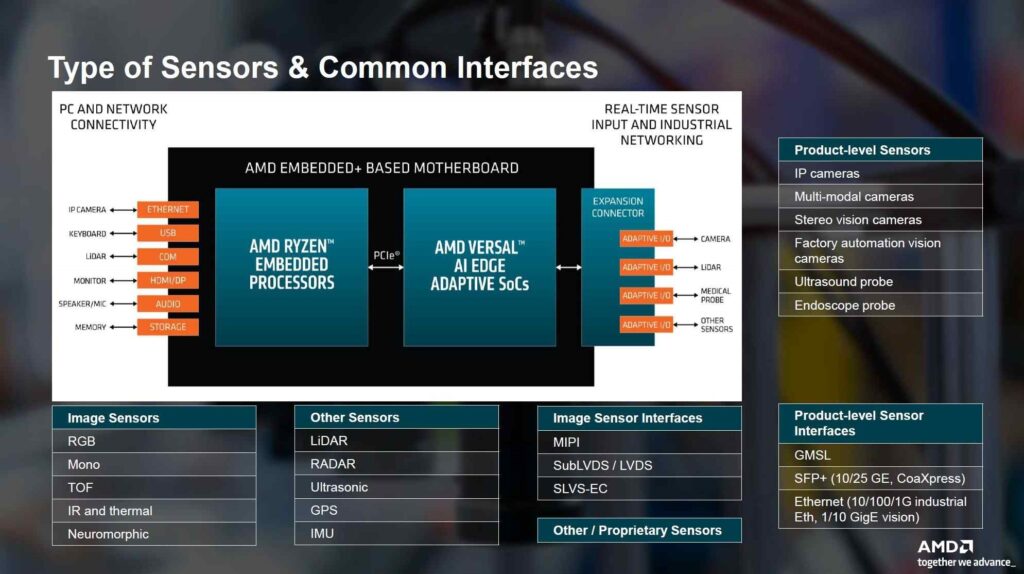
- One benefit of the platform is how adaptable it is in managing various kinds of inputs and outputs.
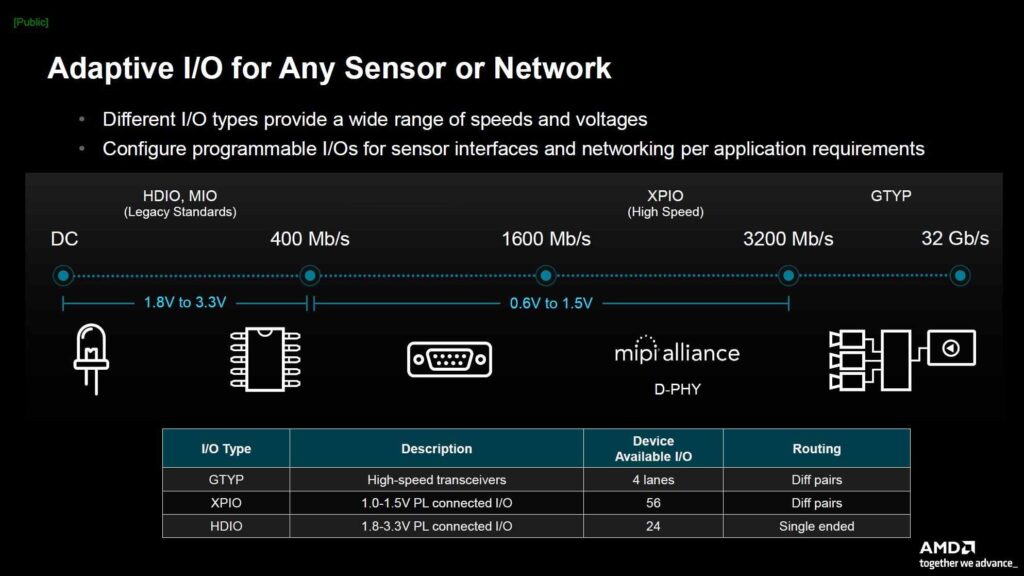
- If you like, you can go for an AMD Ryzen Embedded R2314 SoC based on Zen+. Things designed for embedded use tend to stick around for a while. This particular one is planned to be around two years. It comes out in 2022, so it’s only been about two years since it launched, and it still has a long way to go. Plus, Zen+ has been around for about six years already, showing its reliability over time.

Certainly, with the Ryzen Embedded, we have a GPU that also includes display output along with encoding/decoding functions. However, AV1 is not available because it uses older encoding/decoding technology

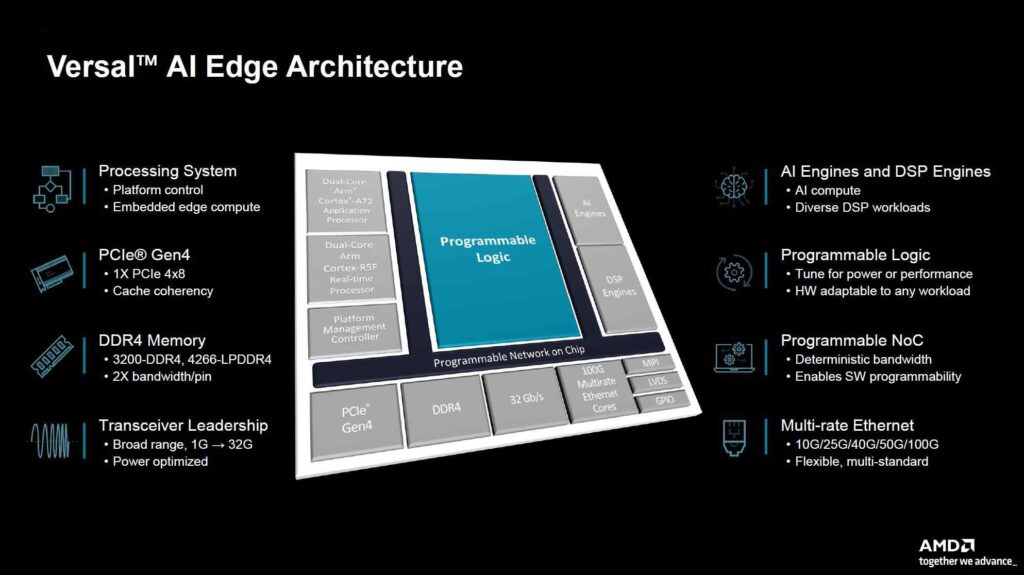
- The Versal AI edge architecture provides many input/output options, Digital signal processing functions, and other features for the platform.
- AMD is teaming up with partners to introduce the new platform today. For instance, the Sapphire VPR-4616-MB comes with both the AMD Versal AI Edge 2302 and the AMD Ryzen Embedded R2314. It’s like a regular computer but also a slot for adding extra boards for input and output.

- This is a significant aspect of the AMD Embedded+ Narrative. The goals is to shorten the time it takes for people to bring their solution to market by simplifying the process of combining AMD’s Embedded x86 and FPGA offerings.
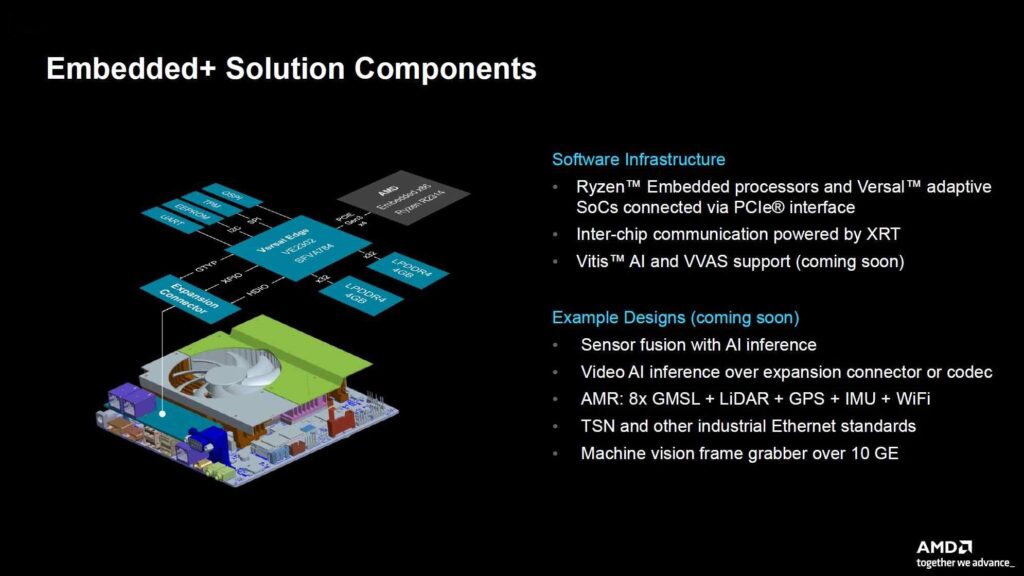
- AMD intends to provide a pre-assembled infrastructure option for this solution, along with a version that cab be fully customized according to induvial needs.

- The concept behind Embedded+ goes beyond just the AMD Ryzen Embedded R2314 and Versal AI Edge 2302. AMD envisions this covering various generations of embedded CPUs and different types of FPGA models.
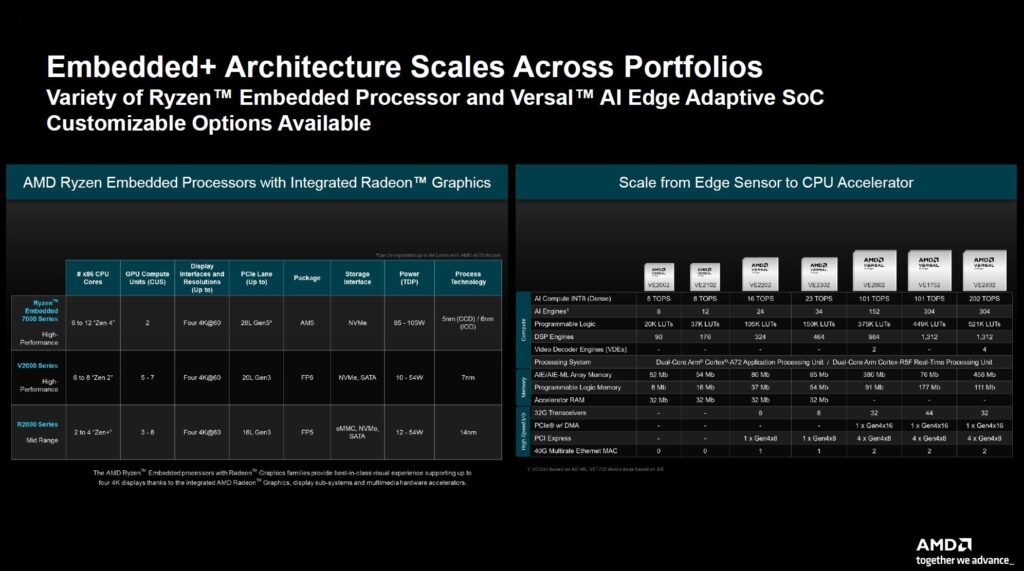
AMD also has Zen 2 and Zen 4 embedded CPUs that it can combine with bigger FPGAs.
FAQs
What is AMD Embedded segment?
The Ryzen Embedded 7000 series processors are crafted to provide top-notch processing power, advanced graphics features, and variety of input/output choices. This versatility makes them ideal for many industrial uses, such as industrial computers workstations, servers at the edge of networks, robots and system for machine vision.
What is Embedded+ Architecture?
The basic of an embedded system has three main parts hardware, software, and applications. The hardware part is all about physical stuff like processors, input-output devices (like buttons or sensors) and memory. Then there’s the software part, which includes the operating system (like Windows or Linux), drivers (which helps the hardware and software talk to each other), and middleware (which helps different software components work together).
What function does embedded design serve?
Embedded systems are built to handle a specific job within a device. Usually, they’re programmed to keep doing that job over and over. However, some advanced embedded systems can do more than just one task. They are capable of running whole operating systems, which means they can control many different jobs within the device.
What role does the CPU play in an embedded system?
An embedded processor is like the boss of a device, making sure it does what it’s supposed to do. It’s a special kind of microprocessor, made specifically for embedded systems. These processors aren’t super fancy, but they are really good at what they do. They’re designed to use as little power as possible, which is important for many devices that need to run for a long time without being plugged in.
What is the difference between CPU and embedded processor?
Embedded processors are usually pretty basic in how they’re made. They don’t have lot of computing power have a lot of computing power or fancy features, and they don’t need much power to work. Basically, they are just a small computer chip that gets put into a device to help it run smoothly. You might have heard about something called “RISC architecture,” which is a way of designing processors to be more efficient.